by Dr. Jaydeep T. Vagh
What is Computer(Common Operating Machine Purposely Used for Technological and Educational Research.)?
Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as input from the user and processes these data under the control of set of instructions (called program) and gives the result (output) and saves output for the future use. It can process both numerical and non-numerical (arithmetic and logical) calculations.
A Computer has Four functions
- Input
- Processing
- Output
- Storage
Input (Data):
Input is the raw information entered into a computer from the input devices. It is the collection of letters, numbers, images etc.
Process:
Process is the operation of data as per given instruction. It is totally internal process of the computer system.
Output:
Output is the processed data given by computer after data processing. Output is also called as Result. We can save these results in the storage devices for the future use.
Computer System
COMPUTER SYSTEM = HARDWARE + SOFTWARE+ USER
All of the components of a computer system can be summarized with the simple equations.
• Hardware = Internal Devices + Peripheral Devices
Software = Set of Programs Programs
USER = Person, who operates computer.
Generations Of Computer
The first generation computers used vaccum tubes & machine language was used for giving the
instructions. These computers were large in size & their programming was difficult task. The electricity consumption was very high. Some computers of this generation are ENIAC, EDVAC, EDSAC & UNIVAC-1
Second Generation (1956-63)
In 2 nd generation computers, vaccum tubes were replaced by transistors. They required only 1/10 of power required by tubes. This generation computers generated less heat & were reliable. The first operating system developed in this generation.
The Third Generation (1964-71)
The 3 rd generation computers replaced transistors with Integrated circuit known as chip. From Small scale integrated circuits which had 10 transistors per chip, technology developed to MSI circuits with 100 transistors per chip. These computers were smaller, faster & more reliable. High level languages invented in this generation.
The fourth Generation (1972- present)
LSI & VLSI were used in this generation. As a result microprocessors came into existence. The
computers using this technology known to be Micro Computer. High capacity hard disk were invented.There is great development in data communication.
The Fifth Generation (Present & Beyond)
Fifth generation computing devices, based on artificial intelligence, are still in development, though there are some applications, such as voice recognition, that are being used today. The use of parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial intelligence a reality. Quantum computation and molecular and nanotechnology will radically change the face of computers in years to come.
ARCHITECTURE OF COMPUTER
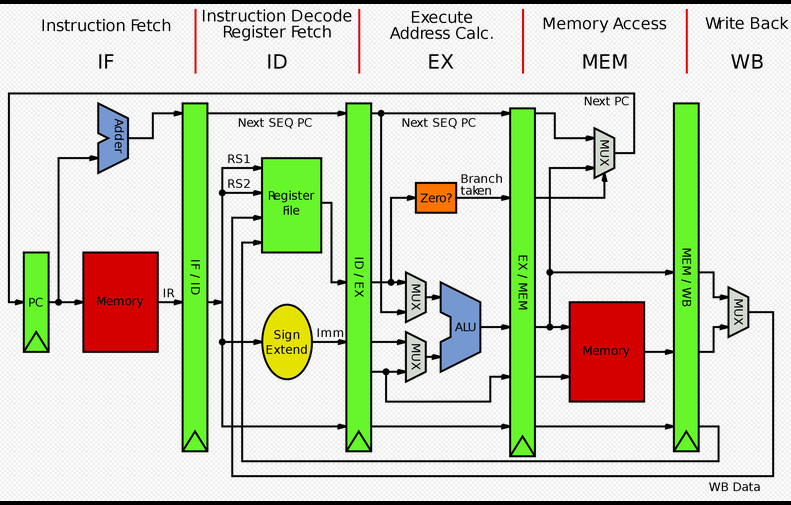


Input Devices: Those devices which help to enter data into computer system. Eg. Keyboad, Mouse, Touchscreen, Barcode Reader, Scanner, MICR, OMR etc.
Output Devices: Those devices which help to display the processed information. Eg. Monitor, Printer, Plotter, Projector
The main component to make a computer operate is the computer chip or microprocessor. This is referred to as the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and is housed in the computer case. Together, they are also called the CPU. It performs arithmetic and logic operations. The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the device that interprets and executes instructions


It facilitates the remembrance power to computer system. It refers to the physical devices
used to store programs (sequences of instructions) or data (e.g. program state information) on a temporary or permanent basis for use in a computer or other digital electronic device. The term primary memory is used for the information in physical systems which are fast (i.e. RAM), as a distinction from secondary memory, which are physical devices for program and data storage which are slow to access but offer higher memory capacity. Primary memory stored on secondary memory is called virtual memory. Primary Memory can be categorized as Volatile Memory & Non-Volatile
Memory.
RAM means Random Access Memory ( Read/ Write Memory ). It‘s known as Volatile Memory. Volatile memory is computer memory that requires power to maintain the stored information. Most modern semiconductor volatile memory is either Static RAM or dynamic RAM.
SRAM retains its contents as long as the power is connected and is easy to interface to but uses six transistors per bit.
Dynamic RAM is more complicated to interface to and control and needs regular refresh cycles to prevent its contents being lost. However, DRAM uses only one transistor and a capacitor per bit, allowing it to reach much higher densities and, with more bits on a memory chip, be much cheaper per bit. SRAM is not worthwhile for desktop system memory, where DRAM dominates, but is used for their cache memories
ROM means Read Only Memory. Non-volatile memory is computer memory that can retain the stored
Cache memory is random access memory (RAM) that a computer microprocessor can access more quickly than it can access regular RAM. As the microprocessor processes data, it looks first in the cache memory and if it finds the data there (from a previous reading of data), it does not have to do the more time-consuming reading of data from larger memory. It is of two types- L1 cache is on the same chip as the microprocessor. L2 is usually a separate static RAM (SRAM) chip.
Blu-ray (not Blue-ray) also known as Blu-ray Disc (BD), is the name of a new optical disc
format. The format offers more than five times the storage capacity of traditional DVDs and can hold up to 25GB on a single-layer disc and 50GB on a dual-layer disc. While current optical disc technologies such as DVD, DVD±R, DVD±RW, and DVD-RAM rely on a red laser to read and write data, the new format uses a blue-violet laser instead, hence the name Blu-ray.
| S.No. | Unit & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Kilobyte (KB) 1 KB = 1024 Bytes |
| 2 | Megabyte (MB) 1 MB = 1024 KB |
| 3 | GigaByte (GB) 1 GB = 1024 MB |
| 4 | TeraByte (TB) 1 TB = 1024 GB |
| 5 | PetaByte (PB) 1 PB = 1024 TB |
The process of loading the system files of the operating system from the disk into the computer memory to complete the circuitry requirement of the computer system is called booting.
Types of Booting:
Cold Booting: If the computer is in off state and we boot the computer by pressing the power
switch ̳ON‘ from the CPU box then it is called as cold booting.
Warm Booting:
If the computer is already ̳ON‘ and we restart it by pressing the ̳RESET‘
button from the CPU box or CTRL, ALT and DEL key simultaneously from the keyboard then
it is called warm booting.
Types of Computer On the basis of working principle
An analog computer is a form of computer that uses continuous physical phenomena such as
electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities to model the problem being solved.
Eg: Thermometer, Speedometer, Petrol pump indicator, Multimeter
A computer that performs calculations and logical operations with quantities represented as digits, usually in the binary number system.
c) Hybrid Computer (Analog + Digital)
A combination of computers those are capable of inputting and outputting in both digital and analog signals. A hybrid computer system setup offers a cost effective method of performing complex simulations. The instruments used in medical science lies in this category.
On the basis of Size
The fastest type of computer. Super Computers are very expensive and are employed for
specialized applications that require immense amounts of mathematical calculations. For example, weather forecasting requires a supercomputer. Other uses of supercomputers include animated graphics, fluid dynamic calculations, nuclear energy research, and petroleum exploration. PARAM, Pace & Flosolver are the supercomputer made in india
A very large and expensive computer capable of supporting hundreds, or even thousands, of
users simultaneously. In the hierarchy that starts with a simple microprocessor (in watches, for example) at the bottom and moves to supercomputers at the top, mainframes are just below supercomputers. In some ways, mainframes are more powerful than supercomputers because they support more simultaneous programs. But supercomputers can execute a single program faster than a mainframe.
A midsized computer. In size and power, minicomputers lie between workstations and mainframes. In the past decade, the distinction between large minicomputers and small mainframes has blurred, however, as has the distinction between small minicomputers and workstations. But in general, a minicomputer is a multiprocessing system capable of supporting from 4 to about 200 users simultaneously. Generally, servers are comes in this category.
i. Desktop Computer: a personal or micro-mini computer sufficient to fit on a desk.
ii. Laptop Computer: a portable computer complete with an integrated screen and keyboard. It
is generally smaller in size than a desktop computer and larger than a notebook computer.
iii. Palmtop Computer/Digital Diary /Notebook /PDAs: a hand-sized computer. Palmtops have
no keyboard but the screen serves both as an input and output device
A terminal or desktop computer in a network. In this context, workstation is just a generic term for a user’s machine (client machine) in contrast to a “server” or “mainframe.”
Software, simply are the computer programs. The instructions given to the computer in the form of a program is called Software. Software is the set of programs, which are used for different purposes. All the programs used in computer to perform specific task is called Software.
- System software:
a) Operating System Software
DOS, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Unix/Linux, MAC/OS X etc.
b) Utility Software
Windows Explorer (File/Folder Management), Compression Tool, Anti-Virus Utilities, Disk
Defragmentation, Disk Clean, BackUp, WinZip, WinRAR etc…
c) Language Processors
Compiler, Interpreter and Assembler - Application software:
a) Package Software
Ms. Office 2003, Ms. Office 2007, Macromedia (Dreamweaver, Flash, Freehand), Adobe
(PageMaker, PhotoShop)
b) Tailored or Custom Software
School Management system, Inventory Management System, Payroll system, financial system
Operating system is a platform between hardware and user which is responsible for the management and coordination of activities and the sharing of the resources of a computer. It hosts the several applications that run on a computer and handles the operations of computer hardware.
Functions of Operating System
Operating system performs the following functions;
1. Booting
Booting is a process of starting the computer operating system starts the computer to work. It checks the computer and makes it ready to work.
2. Memory Management
It is also an important function of operating system. The memory cannot be managed without operating system. Different programs and data execute in memory at one time. if there is no operating system, the programs may mix with each other. The system will not work properly.
3. Loading and Execution
A program is loaded in the memory before it can be executed. Operating system provides the facility to load programs in memory easily and then execute it.
4. Data Security
Data is an important part of computer system. The operating system protects the data stored on the computer from illegal use, modification or deletion.
5. Disk Management
Operating system manages the disk space. It manages the stored files and folders in a proper way.
6. Process Management
CPU can perform one task at one time. if there are many tasks, operating system decides which task should get the CPU.
7. Device Controlling
operating system also controls all devices attached to computer. The hardware devices are controlled with the help of small software called device drivers.
8. Printing Controlling
Operating system also controls printing function. It a user issues two print commands at a time, it does not mix data of these files and prints them separately.
9. Providing Interface
It is used in order that user interface acts with a computer mutually. User interface controls how you input data and instruction and how information is displayed on screen. The operating system offers two types of the interface to the user;
- Graphical-line interface: It interacts with of visual environment to communicate with the computer. It uses windows, icons, menus and other graphical objects to issues commands.
- Command-line interface: it provides an interface to communicate with the computer by typing commands.
Types of Operating System:
1) Real-time Operating System:
It is a multitasking operating system that aims at executing
real-time applications. Example of Use: e.g. control of nuclear power plants, oil refining,
chemical processing and traffic control systems, air
Provides a platform for only one user at a time. They are popularly
associated with Desk Top operating system which run on standalone systems where no user
accounts are required. Example: DOS.
Provides regulated access for a number of users by maintaining a
database of known users.Refers to computer systems that support two or more simultaneous
users. Another term for multi-user is time sharing. Ex: All mainframes are multi-user systems.
Example: Unix
4)Multi-tasking and Single-tasking Operating Systems:
When a single program is allowed to
run at a time, the system is grouped under the single-tasking system category, while in case
the operating system allows for execution of multiple tasks at a time, it is classified as a multi-
tasking operating system.
5)Distributed Operating System:
An operating system that manages a group of independent
computers and makes them appear to be a single computer is known as a distributed
operating system. Distributed computations are carried out on more than one machine. When
computers in a group work in cooperation, they make a distributed system.
Two Special characters, „?‟(question mark) and „*‟ (asterisk) are called wild cards in windows. They are useful in searching files because they give flexibility in specifying paths and files.
The ? wild card A question mark (?) in a filename or file name extension means that any one or none character can occupy that position. For ex. Memo?.doc would represent Memo.doc, Memo3.doc, Memo9.doc etc.
i.e., any file starting with Memo following by exactly any one or none character and with an extension .doc.
The * wild card
The * (asterisk) replaces any number of characters. Ex. A.exe will list Ab.exe, Abc.exe, Answer.exe etc. As A.exe means a followed by any number of characters (but length should not exceed eight in number) and extension .exe.
Commonly used operating system
UNIX:
Pronounced yoo-niks, a popular multi-user, multitasking operating system developed at Bell Labs in the early 1970s. UNIX was one of the first operating systems to be written in a high-level programming language, namely C. This meant that it could be installed on virtually any computer for which a C compiler existed.
Pronounced lee-nucks or lih-nucks. A freely-distributable open source operating system that runs on a number of hardware platforms. The Linux kernel was developed mainly by Linus Torvalds and it is based on Unix. Because it’s free, and because it runs on many platforms, including PCs and Macintoshes, Linux has become an extremely popular alternative to proprietary operating systems. (see the https://www.linux.org/ )
Microsoft Windows is a series of graphical interface operating systems developed,
marketed, and sold by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). [2] Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world’s personal computer market with over 90% market share, overtaking Mac OS, which had been introduced in 1984.The most recent client version of Windows is Windows 7; the most recent server version is Windows Server 2008 R2; the most recent mobile version is Windows Phone 7.5
Solaris is a Unix operating system originally developed by Sun Microsystems. It
superseded their earlier SunOS in 1993. Oracle Solaris, as it is now known, has been owned by
Oracle Corporation since Oracle’s acquisition of Sun in January 2010.
BOSS (Bharat Operating System Solutions) GNU/Linux distribution developed by C-DAC
(Centre for Development of Advanced Computing) derived from Debian for enhancing the use of Free/ Open Source Software throughout India. This release aims more at the security part and comes with an easy to use application to harden your Desktop.
A mobile operating system, also called a mobile OS, is an operating system that is
specifically designed to run on mobile devices such as mobile phones, smartphones, PDAs, tablet computers and other handheld devices. The mobile operating system is the software platform on top of which other programs, called application programs, can run on mobile devices.
Android is a Linux-based mobile phone operating system developed by Google.
Android is unique because Google is actively developing the platform but giving it away for free
to hardware manufacturers and phone carriers who want to use Android on their devices.
Symbian is a mobile operating system (OS) targeted at mobile phones that offers a
high-level of integration with communication and personal information management (PIM)
functionality. Symbian OS combines middleware with wireless communications through an
integrated mailbox and the integration of Java and PIM functionality (agenda and contacts).
The Symbian OS is open for third-party development by independent software vendors,
enterprise IT departments, network operators and Symbian OS licensees.
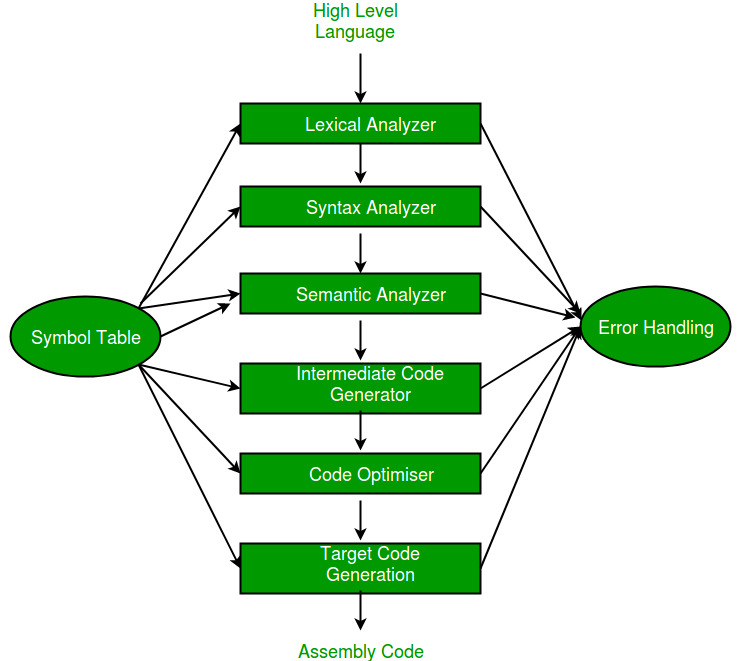
Since a computer hardware is capable of understanding only machine
level instructions, So it is necessary to convert the HLL into Machine Level Language. There are three
A. Compiler:
It is translator which coverts the HLL language into machine language in one go.
Source program in High Level Language get converted into Object Program in Machine Level
Language.
B. Interpreter:
It is a translator which converts the HLL language into machine language line by
line. It takes one statement of HLL and converts it into machine code which is immediately
executed. It eliminate the need of separate compilation/run. However, It is slow in processing
as compare to compiler.
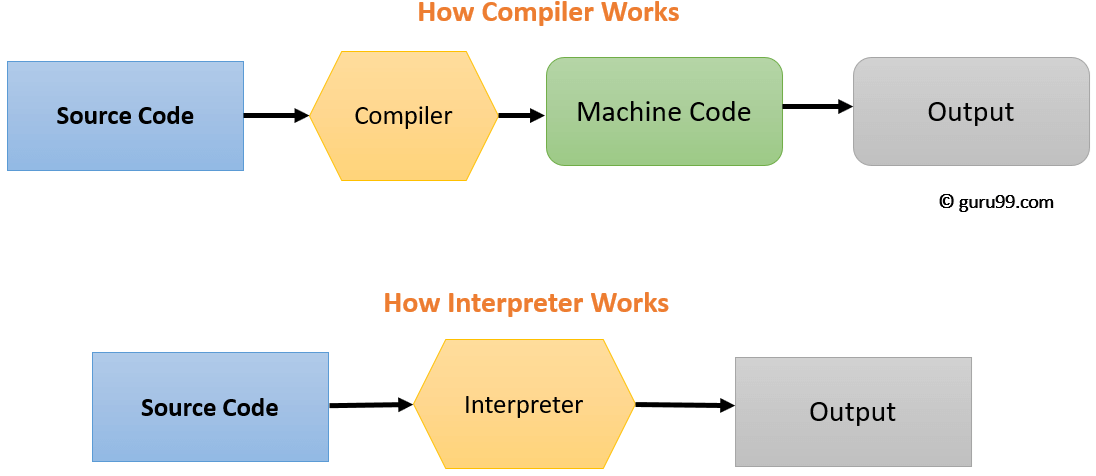
C. Assembler
It translate the assembly language into machine code.
A microprocessor is a semiconductor chip, which is manufactured using the Large Scale integration (LSI) or Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI), which comprises Arithmetic Logic Unit, Control unit and Central Processing Unit (CPU) fabricated on a single chip.
A register is a very small amount of very fast memory that is built into the CPU (central processing unit) in order to speed up its operations by providing quick access to commonly used
values. All data must be represented in a register before it can be processed. For example, if two numbers are to be multiplied, both numbers must be in registers, and the result is also placed in a register.
Bus:
A collection of wires through which data is transmitted from one part of a computer to another. You can think of a bus as a highway on which data travels within a computer. When used in reference to personal computers, the term bus usually refers to internal bus. This is a bus that connects all the internal computer components to the CPU and main memory. All buses consist of two parts — an address bus and a data bus. The data bus transfers actual data whereas the address bus transfers information about where the data should go. The control bus is used by the CPU to direct and monitor the actions of the other functional areas of the computer. It is used to transmit a variety of individual signals (read, write, interrupt, acknowledge, and so forth) necessary to control and coordinate the operations of the computer. The size of a bus, known as its width, is important because it determines how much data can be transmitted at one time. For example, a 16-bit bus can transmit 16 bits of data, whereas a 32-bit bus can transmit 32 bits
Also called clock rate, the speed at which a microprocessor executes instructions.
Every computer contains an internal clock that regulates the rate at which instructions are executed and synchronizes all the various computer components. The CPU requires a fixed number of clock ticks (or clock cycles) to execute each instruction. The faster the clock, the more instructions the CPU can execute per second.
Clock speeds are expressed in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz ((GHz).
16 bit Microprocessor: It indicates the width of the registers. A 16-bit microprocessor can process data and memory addresses that are represented by 16 bits. Eg. 8086 processor
32 bit Microprocessor: It indicates the width of the registers. A 32-bit microprocessor can process data and memory addresses that are represented by 32 bits. Eg. Intel 80386 processor, Intel 80486
64 bit Microprocessor: It indicates the width of the registers; a special high-speed storage area within the CPU. A 32-bit microprocessor can process data and memory addresses that are
represented by 32 bits. Eg. Pentium dual core, core 2 duo.
128 bit Microprocessor: It indicates the width of the registers. A 128-bit microprocessor can
process data and memory addresses that are represented by 128 bits. Eg. Intel core i7
Difference between RISC & CISC architecture
RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing):
- RISC sytem has reduced number of instructions.
- Performs only basic functions.
- All HLL support is done in software.
- All operations are register to register
CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computing):
- A large and varied instruction set.
- Performs basic as well as complex functions.
- All HLL support is done in Hardware.
- Memory to memory addressing mode
EPIC (Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing):
It is a 64-bit microprocessor instruction set, jointly defined and designed by Hewlett Packard and Intel, that provides up to 128 general and floating point unit registers and uses speculative loading, predication, and explicit parallelism to accomplish its computing tasks. By comparison, current 32-bit CISC and RISC microprocessor architectures depend on 32-bit registers, branch prediction, memory latency, and implicit parallelism, which are considered a less efficient approach in microarchitecture
design.
A port is an interface between the motherboard and an external device. Different types of port are available on motherboard as serial port, parallel port, PS/2 port, USB port, SCSI port etc. Serial port(COM Port): A serial port transmit data one bit at a time. Typically on older PCs, a modem, mouse, or keyboard would be connected via serial ports. Serial cables are cheaper to make than parallel cables and easier to shield from interference. Also called communication port.
It supports parallel communication i.e. it can send several bits
simultaneously.It provides much higher data transfer speed in comparison with serial port. Also called Line Printer Port.
It is a newer type of serial connection that is much faster than the old serial ports. USB is also much smarter and more versatile since it allows the “daisy chaining” of up to 127 USB peripherals connected to one port. It provides plug & play communication.
Release versions
| Name | Release date | Maximum transfer rate | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| USB 0.7 | November 11, 1994 | ? | Pre-release |
| USB 0.8 | December 1994 | ? | Pre-release |
| USB 0.9 | April 13, 1995 | Full Speed (12 Mbit/s) | Pre-release |
| USB 0.99 | August 1995 | ? | Pre-release |
| USB 1.0-RC | November 1995 | ? | Release Candidate |
| USB 1.0 | January 15, 1996 | Full Speed (12 Mbit/s), Low Speed (1.5 Mbit/s) | |
| USB 1.1 | August 1998 | Full Speed (12 Mbit/s)[35] | |
| USB 2.0 | April 2000 | High Speed (480 Mbit/s) | |
| USB 3.0/3.1 Gen 1/3.2 Gen 1×1 | November 2008 | Superspeed USB (5 Gbit/s) | Also referred to as USB 3.1 Gen 1[27] and USB 3.2 Gen 1×1 |
| USB 3.1 Gen 2/3.2 Gen 2×1 | July 2013 | Superspeed USB (10 Gbit/s) | Includes new USB 3.1 Gen 2[27] which is later also named USB 3.2 Gen 2×1 |
| USB 3.2 Gen 1×2 | August 2017 | Superspeed USB (10 Gbit/s) | Includes new USB 3.2 Gen 1×2 |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 | August 2017 | Superspeed USB (20 Gbit/s) | Includes USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 multi-link modes[36][failed verification] |
| USB4 | TBD Estimated TBA | (40 Gbit/s) |
USB hardware § USB Power Delivery (USB PD)
| Release name | Release date | Max. power | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| USB Battery Charging 2.0 | 2007-03-08 | 5 V, 1.5 A | |
| USB Battery Charging 2.1 | 2009-04-15 | ? | |
| USB Battery Charging 2.3 | 2010-12-07 | 5 V, 5 A | |
| USB Power Delivery revision 1.0 (version 1.0) | 2012-07-05 | 20 V, 5 A | Using FSK protocol over bus power (VBUS) |
| USB Power Delivery revision 1.0 (version 1.3) | 2014-03-11 | ? | |
| USB-C 2.0 | 2014-08-11 | 5 V, 3 A | New connector and cable specification |
| USB Power Delivery revision 2.0 (version 1.0) | 2014-08-11 | 20 V, 5 A | Using BMC protocol over communication channel (CC) on USB-C cables. |
| USB-C 4.2 | 2015-04-03 | 5 V, 3 A | |
| USB Power Delivery revision 2.0 (version 1.1) | 2015-05-07 | 20 V, 5 A | |
| USB Power Delivery revision 2.0 (version 1.2) | 2016-03-25 | 20 V, 5 A | |
| USB Power Delivery revision 2.0 (version 1.3) | 2017-01-12 | 20 V, 5 A | |
| USB Power Delivery revision 3.0 (version 1.1) | 2017-01-12 | 20 V, 5 A | |
| USB Power Delivery revision 3.0 (version 1.2) | 2018-06-21 | 20 V, 5 A | [37] |
S
Keyboard and mouse ports may be combined into a single port which can be used to connect both by splitter cable. Sometimes, keyboard Data for splitter cable. Sometimes, keyboard Clock for splitter cable.PS/2 ports are special ports for connecting the keyboard and mouse to some PC systems. This type of port was invented by IBM
The IEEE 1394 interface, developed in late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple as
FireWire, is a serial bus interface standard for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. The 1394 interface is comparable with USB and often those two technologies are considered together, though USB has more market share.
An IR port is a port which sends and receives infrared signals from other devices. It is a wireless type port with a limited range of 5-10ft.
Bluetooth uses short-range radio frequencies to transmit information from fixed and mobile devices. These devices must be within the range of 32 feet, or 10 meters for Bluetooth to effectively work. A Bluetooth port enables connections for Bluetooth-enabled devices for synchronizing. Typically there are two types of ports: incoming and outgoing. The incoming port enables the device to receive connections from Bluetooth devices while the outgoing port makes connections to Bluetooth devices.
Internal Storage encoding of Characters:
ASCII( American standard code for information interchange)
ASCII code is most widely used
alphanumeric code used in computers. It is a 7- bit code, and so it has 2 7 =128 possible code groups. It represents all of the standard keyboard characters as well as control functions such as Return & Linefeed functions.
ISCII( Indian standard code for information interchange)
To use the Indian language on
computers, ISCII codes are used. It is an 8-bit code capable of coding 256 characters. ISCII code retains all ASCII characters and offers coding for Indian scripts also.
It is a universal coding standard which provides a unique number for every character, no matter what the platform, no matter what the program, no matter what the language. Unicode version 3.1 represented 94,140 characters.
Numeral system
Decimal Number system composed of 10 numerals or symbols. These numerals are 0 to 9. Using these symbols as digits we can express any quantity. It is also called base-10 system. It is a positional value system in which the value of a digit depends on its position. These digits can represent any value, for example: (754) 10 .
The value is formed by the sum of each digit, multiplied by the base (in this case it is 10 because there are 10 digits in decimal system) in power of digit position (counting from zero):
In Binary Number system there are only two digits i.e. 0 or 1. It is base-2 system. It can be used to represent any quantity that can be represented in decimal or other number system. It is a positional value system, where each binary digit has its own value or weight expressed as
power of 2.
How to convert decimal to binary.
Conversion steps:
- Divide the number by 2.
- Get the integer quotient for the next iteration.
- Get the remainder for the binary digit.
- Repeat the steps until the quotient is equal to 0.
| Division by 2 | Quotient | Remainder | Bit # |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13/2 | 6 | 1 | 0 |
| 6/2 | 3 | 0 | 1 |
| 3/2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 1/2 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
So 1310 = 11012
Example #2
Convert 17410 to binary:
| Division by 2 | Quotient | Remainder | Bit # |
|---|---|---|---|
| 174/2 | 87 | 0 | 0 |
| 87/2 | 43 | 1 | 1 |
| 43/2 | 21 | 1 | 2 |
| 21/2 | 10 | 1 | 3 |
| 10/2 | 5 | 0 | 4 |
| 5/2 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| 2/2 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
| 1/2 | 0 | 1 | 7 |
So 17410 = 101011102
How to convert binary to decimal
For binary number with n digits:
dn-1 … d3 d2 d1 d0
The decimal number is equal to the sum of binary digits (dn) times their power of 2 (2n):
decimal = d0×20 + d1×21 + d2×22 + …
Find the decimal value of 1110012:
| binary number: | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| power of 2: | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 |
1110012 = 1⋅25+1⋅24+1⋅23+0⋅22+0⋅21+1⋅20 = 5710
In Binary Number system there are only two digits i.e. 0 or 1. It is base-2 system. It can be used to represent any quantity that can be represented in decimal or other number system. It is a positional value system, where each binary digit has its own value or weight expressed as
power of 2.
It has eight unique symbols i.e. 0 to 7. It has base of 8. Each octal digit has its own value or weight expressed as a power of 8.
How to convert from octal to decimal
A regular decimal number is the sum of the digits multiplied with 10n.
Example #1
137 in base 10 is equal to each digit multiplied with its corresponding 10n:
13710 = 1×102+3×101+7×100 = 100+30+7
Octal numbers are read the same way, but each digit counts 8n instead of 10n.
Multiply each digit of the hex number with its corresponding 8n.
Example #2
37 in base 8 is equal to each digit multiplied with its corresponding 8n:
378 = 3×81+7×80 = 24+7 = 31
Example #3
7014 in base 8 is equal to each digit multiplied with its corresponding power of 8n:
70148 = 7×83+0×82+1×81+4×80= 3584+0+8+4 = 3596
The hexadecimal system uses base 16. It has 16 possible digit symbols. It uses the digits 0 through 9 plus the letters A,B,C,D,E,F as 16 digit symbols. Each hexadecimal digit has its own value or weight expressed as a power of 16.
How to convert from hex to decimal
A regular decimal number is the sum of the digits multiplied with power of 10.
137 in base 10 is equal to each digit multiplied with its corresponding power of 10:
13710 = 1×102+3×101+7×100 = 100+30+7
Hex numbers are read the same way, but each digit counts power of 16 instead of power of 10.
For hex number with n digits:
dn-1 … d3 d2 d1 d0
Multiply each digit of the hex number with its corresponding power of 16 and sum:
decimal = dn-1×16n-1 + … + d3×163 + d2×162 + d1×161+d0×160
Example #1
3B in base 16 is equal to each digit multiplied with its corresponding 16n:
3B16 = 3×161+11×160 = 48+11 = 5910
Example #2
E7A9 in base 16 is equal to each digit multiplied with its corresponding 16n:
E7A916 = 14×163+7×162+10×161+9×160 = 57344+1792+160+9 = 5930510
Example #3
0.8 in base 16:
0.816 = 0×160+8×16-1 = 0+0.5 = 0.510

nice dr. jaydeep
LikeLike